Miles per gallon (mpg) is a crucial metric for understanding vehicle fuel efficiency. This exploration delves into the factors influencing mpg, from historical trends to technological advancements and government regulations. We’ll also examine how driving habits and maintenance practices impact fuel economy.
Understanding mpg is vital for both environmental and economic reasons. Higher mpg vehicles contribute to lower greenhouse gas emissions and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Consumers can benefit from improved fuel economy by reducing costs at the pump.
Fuel Efficiency Metrics

Fuel efficiency, a critical aspect of vehicle operation, measures how far a vehicle can travel on a given amount of fuel. Understanding these metrics is essential for consumers, policymakers, and environmentalists alike. This section explores various units of measurement, the impact on different vehicle types, and the factors influencing fuel efficiency.Different units are used to quantify fuel efficiency, reflecting varying conventions across regions.
A common metric in the United States is miles per gallon (mpg), while in many other parts of the world, liters per 100 kilometers (L/100km) is prevalent. These units provide comparable information, although a direct conversion requires careful consideration.
Comparison of Fuel Efficiency Units
Different units for measuring fuel efficiency offer comparable but not identical insights. Miles per gallon (mpg) is a common measure in the United States, while liters per 100 kilometers (L/100km) is widely used in other countries. A higher mpg value indicates better fuel efficiency, while a lower L/100km value suggests greater fuel efficiency.
Fuel efficiency, measured in miles per gallon, is a key factor for car owners. Modern advancements like wireless charging pads (car), are impacting how we think about our vehicles, though they don’t directly affect MPG. Ultimately, prioritizing fuel efficiency remains important for minimizing running costs and environmental impact when considering miles per gallon.
Relationship Between Fuel Efficiency and Vehicle Type
Fuel efficiency varies significantly based on the vehicle type. Cars generally exhibit higher fuel efficiency compared to trucks due to their lighter weight and aerodynamic design. Motorcycles, with their smaller engine displacement, tend to have exceptionally high fuel efficiency compared to both cars and trucks. This disparity arises from the fundamental differences in their construction and operational principles.
Factors Influencing Fuel Efficiency
Several factors influence a vehicle’s fuel efficiency. Engine type plays a significant role, with smaller, more efficient engines often delivering better fuel economy. Driving style is crucial; aggressive acceleration and braking reduce efficiency. Tire pressure also significantly affects fuel consumption; under-inflated tires increase rolling resistance, thereby lowering fuel efficiency.
Fuel Efficiency Ratings for Various Vehicle Classes
| Vehicle Class | Average Fuel Efficiency (mpg) |
|---|---|
| Subcompact Cars | 35-45 |
| Compact Cars | 30-40 |
| Mid-size Cars | 25-35 |
| SUVs | 20-30 |
| Light Trucks | 15-25 |
| Minivans | 20-30 |
| Pick-up Trucks | 10-20 |
| Motorcycles | 50-80+ |
This table provides a general overview. Actual fuel efficiency can vary significantly based on individual vehicle models, driving conditions, and driver habits. The provided ranges serve as a guideline for comparing different vehicle types.
Historical Trends
Automotive fuel efficiency has undergone significant transformations over the years, driven by technological advancements and regulatory pressures. Early vehicles often achieved low MPG ratings, primarily due to the limited understanding of engine design and materials. However, consistent efforts in research and development have led to substantial improvements in fuel efficiency, resulting in modern vehicles that are considerably more economical.The evolution of fuel efficiency mirrors the broader development of automotive technology.
Early designs, constrained by engineering limitations, often sacrificed fuel economy for other performance characteristics. As engineering knowledge and materials science progressed, more efficient engine designs and improved aerodynamics became feasible, driving significant advancements in MPG ratings.
Miles Per Gallon Improvements Across Generations
The performance of vehicles has steadily improved over time, impacting fuel economy. Early models, lacking advanced engine technology and lightweight materials, often achieved low MPG ratings. The subsequent generations of vehicles have demonstrated significant improvements, culminating in more fuel-efficient models. Technological advancements in areas like engine design, materials, and aerodynamic efficiency have played a crucial role in this progression.
Impact of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements have had a profound impact on fuel efficiency. Innovations in engine design, including the development of more efficient combustion systems and the adoption of hybrid and electric powertrains, have been instrumental in enhancing fuel economy. For instance, the introduction of turbocharging in the 1980s significantly increased engine power while maintaining relatively high MPG ratings. The transition to lightweight materials, like aluminum and high-strength steel, in recent years has reduced vehicle weight, leading to improved fuel economy.
Key Events and Regulations
Several key events and regulations have profoundly influenced fuel efficiency standards. The introduction of stricter emission standards, often coupled with fuel economy mandates, has pushed manufacturers to develop more fuel-efficient vehicles. The landmark Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) standards in the United States, for example, have mandated a minimum fuel economy average for all vehicles sold within a specific period, significantly impacting the design and production of vehicles.
Other countries have adopted similar regulations, each contributing to a global trend towards improved fuel efficiency.
Timeline of Milestones in Automotive Fuel Efficiency
| Year | Milestone | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 1970s | Introduction of catalytic converters | Reduced emissions, indirectly improved fuel efficiency. |
| 1980s | Turbocharging becomes more common | Increased power output with relatively high fuel economy. |
| 1990s | Advancements in aerodynamics | Improved fuel economy through reduced drag. |
| 2000s | Increased use of lightweight materials | Reduced vehicle weight, leading to improved fuel economy. |
| 2010s | Rise of hybrid and electric vehicles | Significant leap in fuel efficiency, especially in specific driving conditions. |
These milestones highlight the evolution of automotive technology and its direct impact on fuel economy, demonstrating the continual quest for more sustainable and efficient transportation.
Impact on the Environment
Higher fuel efficiency translates to a significant reduction in the environmental footprint of transportation. This is a crucial factor in mitigating climate change and improving air quality globally. Vehicles consuming less fuel produce fewer emissions, contributing to a healthier planet.Fuel efficiency and its environmental benefits are intricately linked. Lower fuel consumption directly correlates with decreased greenhouse gas emissions, reduced energy consumption, and ultimately, less air pollution.
The positive impacts on the environment are substantial and far-reaching.
Environmental Benefits of Higher MPG
Increased fuel efficiency yields numerous environmental advantages. Lower fuel consumption translates to decreased emissions of greenhouse gases, notably carbon dioxide, which is a primary contributor to global warming. Reduced emissions also contribute to cleaner air, lessening the health risks associated with air pollution. These benefits are crucial in the fight against climate change and for the overall well-being of the planet.
Correlation Between Fuel Efficiency and Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Fuel efficiency and greenhouse gas emissions share an inverse relationship. Higher miles per gallon (MPG) directly correlate with lower emissions of greenhouse gases. This reduction is a critical component in mitigating climate change and its associated impacts. For instance, a vehicle achieving 50 MPG emits significantly less carbon dioxide compared to a vehicle with 20 MPG, all else being equal.
The reduced emissions lead to a smaller carbon footprint for transportation, contributing to a healthier environment.
Impact of Fuel Efficiency on Global Energy Consumption
Higher fuel efficiency reduces the global demand for fossil fuels. More fuel-efficient vehicles require less fuel to travel the same distance, leading to a decrease in overall energy consumption. This decrease in demand can potentially stabilize global energy markets and promote the adoption of renewable energy sources. Countries with high vehicle populations will see notable reductions in fossil fuel dependency as vehicle fleets become more fuel-efficient.
Impact of Fuel Efficiency on Reducing Air Pollution
Fuel efficiency plays a vital role in reducing air pollution. Lower fuel consumption results in decreased emissions of harmful pollutants, such as nitrogen oxides and particulate matter. These pollutants contribute to respiratory problems and other health issues. Improved fuel efficiency, therefore, directly contributes to a healthier environment, especially in urban areas with heavy traffic. This translates to improved air quality and public health.
Consumer Considerations
Maximizing fuel efficiency is crucial for both personal savings and environmental responsibility. Understanding driving habits, vehicle maintenance, and tire management directly impacts a vehicle’s fuel economy. This section provides practical guidance for consumers to optimize their fuel efficiency.Driving habits and maintenance procedures play a significant role in a vehicle’s fuel economy. By implementing small changes in driving style and regular maintenance, consumers can significantly improve their fuel efficiency.
This, in turn, leads to lower fuel costs and a smaller environmental footprint.
Driving Style and Fuel Economy
Driving style significantly impacts a vehicle’s fuel economy. Aggressive acceleration, rapid braking, and excessive idling consume more fuel than a smooth, consistent driving style.
- Aggressive Driving often leads to lower fuel efficiency. Rapid acceleration and braking require more power, increasing fuel consumption. Conversely, maintaining a consistent speed and avoiding sudden maneuvers enhances fuel economy.
- Gentle Acceleration and Deceleration contribute to optimal fuel efficiency. Avoiding rapid acceleration and braking, instead choosing smooth transitions, results in better fuel economy. This approach allows the engine to operate at a more efficient RPM range.
- Cruise Control can improve fuel efficiency, especially on highways. Maintaining a consistent speed reduces the engine’s workload, allowing for more efficient fuel combustion.
- Avoiding Excessive Idling is crucial for fuel economy. Extended periods of idling consume significant fuel without producing meaningful forward progress. If possible, turn off the engine when stopped for extended periods.
Vehicle Maintenance and Fuel Efficiency
Regular vehicle maintenance is essential for optimal fuel efficiency. Ignoring routine upkeep can lead to decreased fuel economy and potentially more significant repair costs down the line.
- Regular Oil Changes ensure proper lubrication of engine components. Insufficient or outdated oil can lead to increased friction and reduced fuel efficiency.
- Air Filter Replacement is important. A clogged air filter restricts airflow, forcing the engine to work harder and consume more fuel.
- Tire Rotation distributes wear evenly, maintaining proper tire pressure and rolling resistance, impacting fuel efficiency.
- Brake System Inspection is crucial. Worn brakes and calipers can cause increased friction, leading to decreased fuel efficiency and potentially affecting braking performance.
Tire Pressure and Inflation
Tire pressure significantly impacts fuel efficiency. Proper tire inflation maintains optimal rolling resistance and minimizes friction.
- Incorrect Tire Pressure leads to increased rolling resistance. This extra friction requires more power from the engine to move the vehicle, thus decreasing fuel economy.
- Proper Tire Inflation reduces rolling resistance, allowing the vehicle to move with less engine effort. This contributes to better fuel efficiency.
- Checking Tire Pressure Regularly is essential. Tire pressure should be checked regularly, ideally monthly, to maintain optimal fuel economy. Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for recommended tire pressure.
- Using a Tire Pressure Gauge ensures accurate pressure readings for accurate tire inflation.
Technological Advancements
Recent years have witnessed significant advancements in automotive technology, directly impacting fuel efficiency. Innovations in engine design, alternative fuel sources, and vehicle electrification are driving improvements in MPG and reducing environmental impact. These advancements represent a crucial shift towards sustainable transportation solutions.
Hybrid Vehicle Technology
Hybrid vehicles combine an internal combustion engine (ICE) with an electric motor. This combination allows for improved fuel economy compared to traditional gasoline-powered cars. The electric motor assists the ICE during acceleration and deceleration, reducing the engine’s workload and fuel consumption. Significant improvements in battery technology have also enhanced hybrid vehicle performance.
- Pros: Hybrid vehicles offer a balance between fuel efficiency and performance. They typically provide a noticeable improvement in MPG compared to conventional cars, while maintaining the convenience of readily available fuel. The reduced reliance on the ICE during routine driving contributes to lower emissions.
- Cons: Hybrid vehicles can be more expensive to purchase than their comparable gasoline-powered counterparts. The hybrid powertrain can be more complex than a traditional ICE, potentially leading to higher maintenance costs. The overall cost-effectiveness depends heavily on fuel prices and driving habits.
Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Electric vehicles (EVs) rely solely on electric motors powered by batteries. The elimination of the internal combustion engine leads to zero tailpipe emissions and, under certain conditions, potentially higher fuel efficiency compared to hybrid or gasoline-powered vehicles. Charging infrastructure is rapidly expanding, making EVs increasingly accessible.
- Pros: EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, reducing air pollution. They often offer higher fuel efficiency than comparable gasoline-powered cars, especially in urban environments with shorter commutes. The potential for lower running costs (depending on electricity prices) is an attractive aspect.
- Cons: The higher initial purchase price of EVs is a significant barrier for some consumers. Range anxiety, the concern over the limited driving range on a single charge, is a common concern. The availability of charging stations and the cost of electricity can affect the overall cost-effectiveness.
Alternative Fuels
Alternative fuels, such as biodiesel and compressed natural gas (CNG), offer potential avenues for improving fuel efficiency. Biodiesel, produced from renewable sources, can be used in some vehicles with minor modifications. CNG offers a relatively clean-burning alternative to gasoline.
- Pros: Biodiesel and CNG offer reduced reliance on fossil fuels. Biodiesel, derived from renewable sources, can contribute to a more sustainable fuel supply. CNG, while not entirely emission-free, typically produces lower emissions compared to gasoline.
- Cons: The availability of infrastructure for alternative fuels, such as refueling stations for biodiesel and CNG, is limited in many regions. The production of some alternative fuels may have environmental implications. The cost of alternative fuels can vary significantly.
Future of Fuel Efficiency Technologies
Continued advancements in battery technology and electric motor design are expected to enhance the performance and range of EVs. The development of more efficient internal combustion engines, coupled with advancements in hybrid systems, will further improve fuel efficiency. Integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning could lead to optimized driving patterns and further fuel savings.
Impact of EVs on Overall Fuel Efficiency Metrics, Miles per gallon
The widespread adoption of EVs is projected to have a significant impact on overall fuel efficiency metrics. The shift away from gasoline-powered vehicles toward electric vehicles will reduce the overall carbon footprint of transportation. The impact on gasoline consumption will depend on factors such as electricity generation sources and the overall energy mix.
Government Regulations
Governments play a crucial role in fostering fuel efficiency by enacting and enforcing regulations. These regulations influence vehicle design, manufacturing processes, and ultimately, the fuel economy of vehicles on the market. By setting standards, governments aim to reduce the environmental impact of transportation and promote the adoption of more efficient technologies.Regulations are essential for driving improvements in fuel economy.
They create a level playing field for manufacturers, incentivizing innovation and the development of more fuel-efficient vehicles. This, in turn, benefits consumers with lower fuel costs and a reduced carbon footprint.
Role of Regulations in Promoting Fuel Efficiency
Government regulations act as a catalyst for improving fuel efficiency. They mandate minimum fuel economy standards for vehicles, encouraging manufacturers to incorporate more fuel-efficient technologies into their designs. This proactive approach directly impacts the development of vehicles that consume less fuel.
Impact of Fuel Economy Standards on Vehicle Design and Production
Fuel economy standards significantly affect vehicle design and production. Manufacturers are compelled to prioritize lightweight materials, aerodynamic shapes, and more efficient engine designs to meet these standards. These design choices influence the overall structure and operation of vehicles, leading to vehicles that are lighter, more streamlined, and better optimized for fuel consumption. The impact is tangible in both the manufacturing process and the end product.
Key Regulations Related to Fuel Efficiency
Fuel economy regulations vary across jurisdictions and evolve over time. These regulations are vital components in the pursuit of improved fuel efficiency.
- The Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) standards in the United States are a prime example of regulations influencing vehicle production. These standards mandate average fuel economy across a manufacturer’s entire fleet of vehicles. Failure to meet these standards can result in penalties.
- European Union regulations also set stringent fuel efficiency targets for automobiles sold within the bloc. These standards are constantly updated to reflect evolving technologies and environmental concerns. Their impact on the European auto industry is profound.
- Similar regulations exist globally, with countries implementing policies to encourage the production and sale of fuel-efficient vehicles. These policies vary based on local conditions and priorities.
Evolution of Fuel Efficiency Regulations
Fuel economy regulations have undergone significant changes over the years. The standards have become increasingly stringent to reflect advancements in technology and evolving environmental concerns.
- Early regulations focused primarily on establishing baseline standards for fuel economy. These early standards often lagged behind technological advancements, leading to a gradual improvement over time.
- Later regulations incorporated more advanced technologies, such as hybrid powertrains and alternative fuels, into the standards. These advancements have been driven by the increasing awareness of environmental impact and the availability of new technologies.
- Current regulations often include provisions for different vehicle classes and fuel types. This approach reflects the diversity of vehicles on the market and the need to tailor regulations to specific circumstances.
Fuel Efficiency in Different Regions: Miles Per Gallon
Global fuel efficiency standards and trends vary significantly, reflecting diverse driving conditions, infrastructure, and economic factors. These variations impact not only vehicle design and manufacturing but also consumer choices and environmental outcomes. Understanding these regional differences is crucial for assessing the overall picture of fuel efficiency progress and future challenges.Fuel efficiency preferences are often influenced by local fuel prices.
In regions with high fuel costs, consumers are more inclined towards vehicles with better fuel economy, while in areas with relatively low fuel prices, the focus might shift towards other factors like performance or vehicle size. This dynamic interplay between price and preference shapes the demand for different vehicle types and ultimately affects regional fuel efficiency trends.
Fuel Efficiency Standards and Trends
Different regions have implemented various fuel efficiency standards, often reflecting specific environmental goals and economic priorities. These standards vary in stringency and scope, leading to notable disparities in fuel economy targets across the globe.
Impact of Local Fuel Prices
Fuel prices play a significant role in shaping consumer preferences for fuel-efficient vehicles. In countries with high fuel costs, consumers are more likely to prioritize vehicles with superior fuel economy. Conversely, in areas with low fuel costs, fuel efficiency might take a backseat to other factors like performance or vehicle size.
Impact of Driving Conditions
Driving conditions significantly affect fuel efficiency. Urban environments with frequent stops and starts, combined with heavy traffic, typically result in lower fuel economy compared to highway driving. Geographical features, such as mountainous terrains, also contribute to variations in fuel efficiency. For example, vehicles operating in hilly regions will consume more fuel due to the increased energy demands for climbing inclines.
These varying driving conditions are crucial to consider when comparing fuel efficiency across different regions.
Average Fuel Efficiency in Different Countries
| Country | Average Fuel Efficiency (estimated MPG) | Year | Driving Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | 25-30 | 2022 | Mix of urban and highway |
| Japan | 35-40 | 2022 | Urban and highway with emphasis on fuel efficiency |
| Europe | 40-50 | 2022 | Mix of urban and highway with emphasis on fuel efficiency |
| China | 20-25 | 2022 | Mix of urban and highway, increasing emphasis on efficiency |
Note: Average fuel efficiency figures are estimates and may vary based on specific vehicle models, driving habits, and testing methodologies. The provided data represents a general comparison.
Fuel Efficiency and Vehicle Types
Fuel efficiency varies significantly across different vehicle types, reflecting design choices and intended use cases. Understanding these variations is crucial for consumers seeking the most suitable vehicle for their needs and environmental impact. Factors like engine type, transmission, aerodynamic design, and overall vehicle weight play a key role in determining fuel economy.
Comparison of Fuel Efficiency Across Vehicle Types
Different vehicle types are engineered with different priorities. Sedans, for instance, prioritize passenger space and fuel efficiency, while SUVs prioritize cargo space and passenger comfort. Trucks, in contrast, prioritize hauling capacity. This difference in design and intended use directly impacts the fuel efficiency of each type. Consequently, fuel economy figures differ across these categories.
Factors Influencing Fuel Efficiency in Specific Vehicle Segments
Several factors influence fuel efficiency within each vehicle segment. For example, in sedans, lighter weight and more efficient engines contribute to better fuel economy. In SUVs, factors like aerodynamic design and the size and type of engine play a crucial role. Trucks, particularly those designed for heavy hauling, often face challenges in achieving high fuel efficiency due to the weight and power demands of their cargo.
Average Fuel Efficiency Figures for Various Vehicle Types
The average fuel efficiency figures provided below are approximations and can vary based on specific models, driving conditions, and individual vehicle maintenance. These values are meant to give a general comparison across different vehicle categories.
| Vehicle Type | Average MPG (estimated) |
|---|---|
| Sedans | 30-40 MPG |
| SUVs | 20-30 MPG |
| Light Trucks | 15-25 MPG |
| Heavy-Duty Trucks | 7-15 MPG |
Vehicle Size and Design Affecting Fuel Economy
Vehicle size and design directly correlate with fuel efficiency. Larger vehicles, such as SUVs and trucks, generally have lower fuel economy compared to smaller vehicles like sedans. This is largely due to the increased weight and drag associated with larger dimensions. Aerodynamic design plays a significant role, with more streamlined designs tending to achieve better fuel economy.
The engine type and transmission choice also affect fuel efficiency within each category.
Fuel Efficiency and Driving Habits
Driving habits significantly impact a vehicle’s fuel economy. Optimizing these habits can lead to substantial savings in fuel costs and a reduced environmental footprint. Understanding the interplay between driving style and fuel consumption is key to maximizing your vehicle’s efficiency.
Aggressive Driving Impacts Fuel Efficiency
Aggressive driving techniques, characterized by rapid acceleration, hard braking, and excessive speed, contribute to lower fuel efficiency. These actions increase engine load and require more fuel to maintain the desired speed or to quickly change the vehicle’s velocity. For instance, rapid acceleration repeatedly stresses the engine, demanding higher fuel consumption to generate the needed power. Similarly, hard braking dissipates kinetic energy as heat, diminishing the efficiency of the vehicle’s motion.
Frequent and abrupt changes in speed disrupt the engine’s optimal operating range, increasing fuel usage.
Consistent Speed and Fuel Consumption
Maintaining a consistent speed, within the recommended range for the vehicle and road conditions, is crucial for maximizing fuel efficiency. The relationship between speed and fuel consumption is often non-linear, meaning the fuel efficiency drops significantly as the speed increases beyond a certain point. Fuel consumption increases exponentially as the speed surpasses this threshold. For example, driving at 70 mph (113 km/h) on a highway can require significantly more fuel than driving at 55 mph (89 km/h).
This difference in fuel consumption is directly correlated with the aerodynamic resistance and engine load at each speed.
Proper Acceleration and Braking Techniques
Proper acceleration and braking techniques contribute significantly to fuel efficiency. Gentle acceleration, allowing the engine to smoothly transition between gears, minimizes fuel waste. Avoiding sudden bursts of acceleration or deceleration is crucial. Anticipating traffic conditions and maintaining a safe following distance enables smoother deceleration and acceleration. Similarly, planned braking, using the engine braking function whenever possible, helps maintain momentum and reduces the need for rapid deceleration.
This technique, often called coasting, allows the vehicle to use less fuel during deceleration.
Optimizing Fuel Efficiency Through Smooth Driving
Smooth driving, characterized by consistent speed and gradual acceleration and braking, is fundamental to maximizing fuel efficiency. Anticipating traffic patterns and maintaining a steady speed profile reduces the frequency of rapid changes in engine load. Maintaining a consistent speed reduces aerodynamic drag, minimizing fuel consumption. Moreover, smooth braking techniques allow the vehicle to use the engine’s regenerative braking to recover energy, further enhancing efficiency.
This strategy helps the driver minimize the need for the brakes to apply forcefully. Smooth driving not only saves fuel but also reduces wear and tear on the vehicle’s components.
Fuel Efficiency and Maintenance
Proper vehicle maintenance is crucial for optimal fuel efficiency. A well-maintained vehicle not only performs better but also uses fuel more effectively, leading to reduced operating costs and a smaller environmental footprint. Neglecting routine maintenance can lead to decreased fuel economy and potentially more significant repair needs down the road.Regular upkeep is a proactive approach to preserving fuel efficiency.
This involves understanding the connection between maintenance tasks and fuel economy, as well as identifying and rectifying potential issues early on. By consistently performing the necessary maintenance procedures, vehicle owners can significantly enhance their fuel efficiency and overall driving experience.
Impact of Tire Pressure on Fuel Efficiency
Tire pressure plays a significant role in fuel economy. Under-inflated tires increase rolling resistance, requiring the engine to work harder to propel the vehicle. This extra effort translates directly to reduced fuel efficiency. Over-inflated tires also contribute to increased rolling resistance, though to a lesser degree than under-inflation. Maintaining the recommended tire pressure, as indicated in the vehicle’s owner’s manual, is essential for optimal fuel economy.
The Role of Air Filters in Fuel Efficiency
Clogged air filters restrict the flow of air to the engine. This restriction can lead to the engine running less efficiently and consuming more fuel. Regular air filter replacement ensures adequate airflow, enabling the engine to operate at its optimal efficiency. This translates directly into better fuel economy. A clean air filter allows the engine to breathe properly, reducing strain and promoting more efficient combustion.
Fuel efficiency, like miles per gallon, is crucial. Modern tech, like an AI-powered dash cam AI-powered dash cam , can potentially offer insights that impact MPG. By monitoring driving habits, these systems might help drivers identify areas for improvement, ultimately boosting their vehicle’s fuel economy.
The Significance of Engine Tune-ups
Engine tune-ups are crucial for maintaining optimal fuel efficiency. A well-tuned engine operates with the correct fuel-air mixture, ensuring efficient combustion and minimizing wasted fuel. Regular tune-ups can identify and resolve potential issues, such as misfiring spark plugs or faulty ignition systems, which can lead to significant fuel consumption increases. This preventative maintenance keeps the engine running smoothly and at peak performance, ultimately improving fuel efficiency.
Maintenance Procedures for Improved Fuel Efficiency
- Regular oil changes: Oil changes are essential for maintaining engine lubrication and preventing wear and tear. Using the correct type and viscosity of oil, as specified in the owner’s manual, is critical for maintaining fuel efficiency.
- Checking and adjusting tire pressure: Regularly checking and adjusting tire pressure to the manufacturer’s recommended specifications ensures minimal rolling resistance and optimized fuel economy.
- Replacing air filters regularly: Regular air filter replacements prevent restriction in airflow, allowing the engine to run smoothly and consume fuel efficiently.
- Performing engine tune-ups: Engine tune-ups ensure proper fuel-air mixture and spark plug function, optimizing fuel combustion and improving overall fuel economy.
- Inspecting and replacing spark plugs: Spark plugs that are worn or damaged can contribute to inefficient combustion and reduced fuel efficiency. Replacing them when needed is vital.
- Checking and maintaining the fuel system: Regular inspection of fuel lines, filters, and injectors can identify and rectify potential issues that lead to fuel wastage.
Identifying and Fixing Fuel Efficiency Problems
Systematic troubleshooting is crucial for identifying fuel-efficiency problems. By following a logical sequence of checks, potential issues can be addressed effectively.
- Monitor fuel consumption: Keep track of fuel consumption over time to detect unusual trends. Comparing recent consumption with historical records helps identify potential problems.
- Inspect for leaks: Regular visual inspections of fuel lines, hoses, and other components can detect leaks that contribute to fuel loss.
- Examine air intake: Inspect the air intake system for obstructions or damage that could hinder airflow and impact fuel efficiency.
- Check for unusual noises: Pay attention to unusual engine noises, as they can indicate underlying issues that may affect fuel economy.
Final Summary
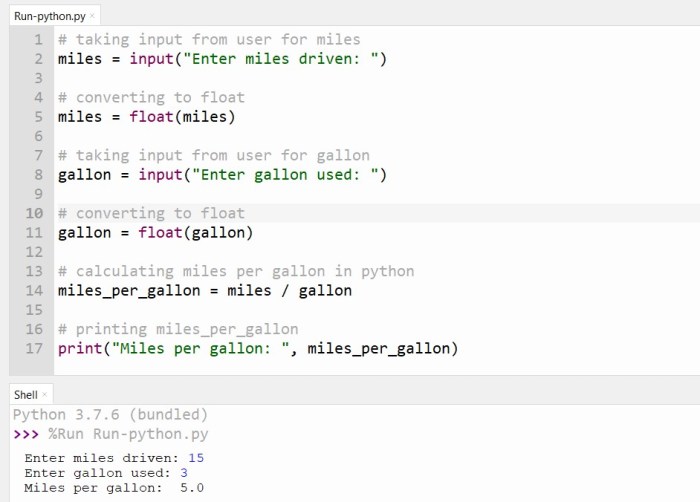
In conclusion, miles per gallon is a multifaceted topic encompassing historical data, technological advancements, environmental impacts, and consumer considerations. We’ve explored how various factors influence fuel efficiency, from engine types to driving styles and government regulations. Ultimately, maximizing mpg is a key element in sustainable transportation and responsible resource management.
FAQ Compilation
What is the average mpg for a new sedan?
Average mpg for new sedans varies significantly based on specific model and engine type, but generally falls between 25-40 mpg.
How does aggressive driving affect mpg?
Aggressive driving, including rapid acceleration and braking, significantly reduces mpg due to increased engine load and friction.
What role do tires play in fuel efficiency?
Proper tire pressure is crucial for fuel efficiency. Under-inflated tires increase rolling resistance, leading to lower mpg.
How do hybrid vehicles impact overall mpg metrics?
Hybrid vehicles often achieve higher mpg than comparable gasoline-powered cars due to their combined electric and gasoline engine systems.





