Interoperable EV apps pave the way for a future where electric vehicle ownership is simplified and enhanced. Imagine a world where charging at any station is intuitive, vehicle diagnostics are easily accessible, and data sharing across apps is seamless. This is the promise of interoperable EV apps, connecting drivers, charging networks, and maintenance services in a unified digital ecosystem.
This exploration dives deep into the concept of interoperability, examining its benefits, challenges, and future potential. We’ll analyze use cases, discuss crucial security considerations, and explore the evolving standards and implementation strategies that will shape the EV landscape.
Defining Interoperability
Interoperable EV apps are crucial for seamless user experiences and broader adoption of electric vehicles. They allow different applications to communicate and share data, enabling features like unified vehicle management and personalized experiences. This is vital for a future where EV ownership is increasingly integrated with various services.Interoperability in this context hinges on standardized communication protocols and data formats.
This allows applications from different vendors to exchange information without requiring extensive custom integrations. This approach is essential for creating a vibrant ecosystem of EV-related services, supporting a wider range of features and capabilities.
Core Principles of Interoperability
Interoperability in EV apps rests on a few fundamental principles. Firstly, shared data formats are essential for ensuring that applications can understand and interpret data from other sources. Secondly, standardized communication protocols enable efficient and reliable data exchange between applications. Thirdly, a well-defined API (Application Programming Interface) provides a clear structure for developers to access and use shared data.
These principles minimize integration complexities and promote compatibility among different EV apps.
Technical Aspects of Data Exchange
Data exchange between EV apps relies on secure and efficient communication channels. This involves protocols like RESTful APIs, which provide a structured way for apps to request and receive data. Security is paramount, requiring authentication and authorization mechanisms to protect sensitive vehicle data. Furthermore, data encryption safeguards exchanged information during transmission. This technical framework ensures data integrity and confidentiality, critical for user trust and system reliability.
Interoperable EV apps are crucial for a seamless EV experience, allowing for easy access to charging and other services. This becomes even more important when considering the potential of battery swapping solutions, like battery swapping , which could drastically reduce charging times and improve range anxiety. Ultimately, the success of widespread EV adoption hinges on the development of these interoperable apps that support these innovative charging alternatives.
Types of Data Exchanged
The range of data shared between EV apps is extensive. It includes real-time charging status, including current charging rate, estimated completion time, and remaining battery level. Diagnostics data, such as vehicle health reports, error codes, and maintenance schedules, are also crucial. Location data, enabling features like optimized routing and parking searches, is a key component. Finally, user preferences and settings for various services and functionalities are essential for personalized experiences.
These diverse data types are vital for creating a holistic and interconnected EV ecosystem.
| Data Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Charging Status | Current charging rate, estimated completion time, remaining battery level | Charging at 3.5 kW, estimated completion in 2 hours, remaining battery 85% |
| Vehicle Diagnostics | Vehicle health reports, error codes, maintenance schedules | Low tire pressure, upcoming brake pad replacement in 1000 miles |
| Location Data | Real-time location, optimized routing, parking searches | Current location: 123 Main Street, optimized route to destination |
| User Preferences | Settings for services and functionalities | Preferred charging station type, preferred payment method |
Benefits of Interoperable EV Apps
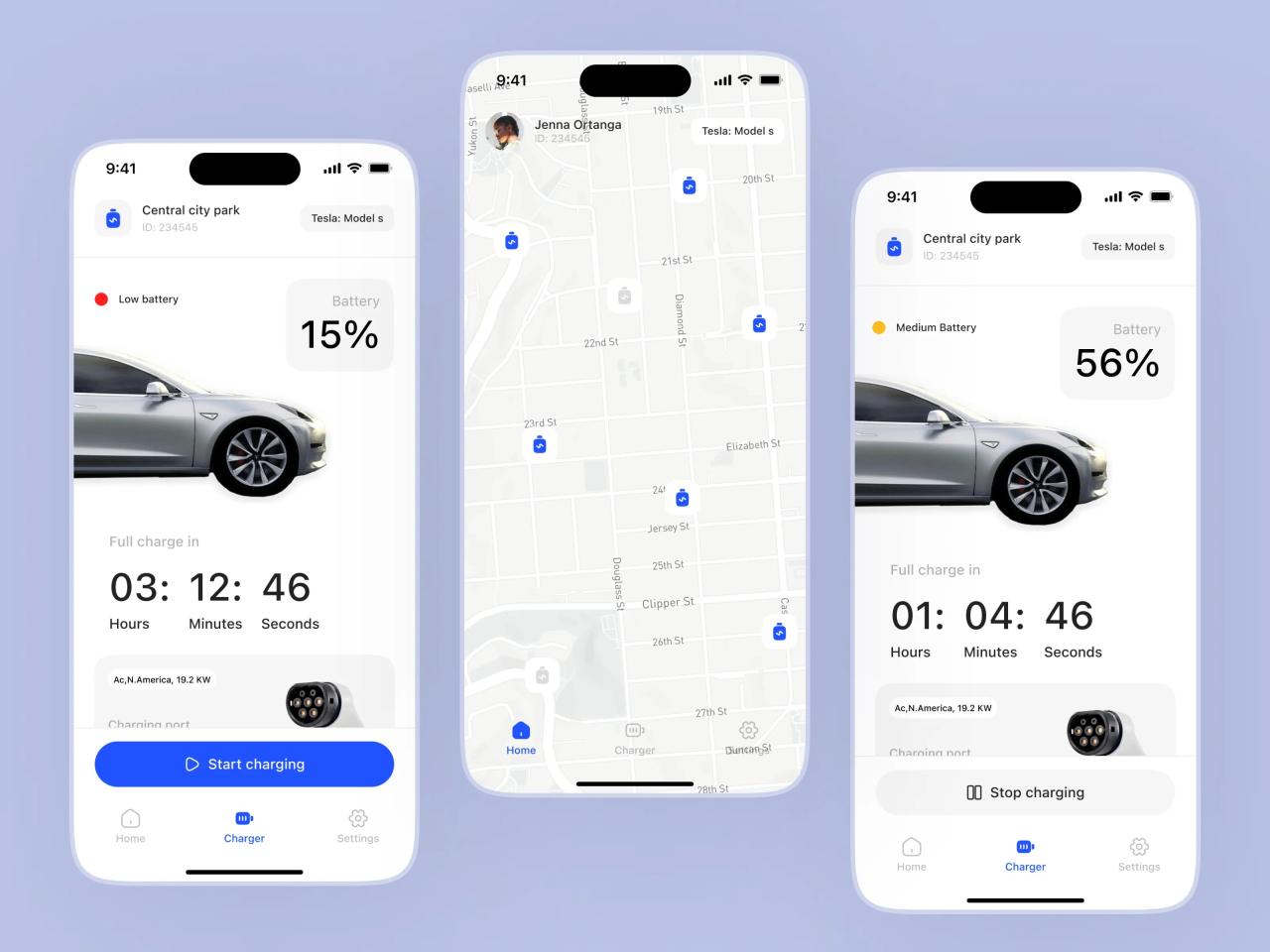
Interoperable EV applications offer significant advantages for all stakeholders involved in the electric vehicle ecosystem. By facilitating seamless communication and data exchange between different platforms, these apps unlock new possibilities for drivers, charging infrastructure providers, and the overall efficiency of EV management. This improved connectivity fosters a more integrated and user-friendly experience for everyone.
Advantages for EV Drivers
Interoperable EV apps provide a consolidated view of charging options and pricing, streamlining the driver experience. Drivers can easily access charging stations, compare rates, and plan routes with confidence, eliminating the need to navigate multiple, disparate apps. This unified platform reduces the cognitive load on drivers, enhancing their overall experience. Real-time updates on charging station availability and pricing directly impact the driver’s decision-making process, improving the efficiency of their journeys.
Enhanced User Experience for EV Owners
Interoperability greatly enhances the user experience for EV owners. A single app can manage charging sessions, payment, and vehicle maintenance, providing a centralized hub for all EV-related tasks. The ability to seamlessly integrate with existing payment systems and vehicle information systems simplifies the process of charging and managing the vehicle. This streamlined approach minimizes the need for constant switching between apps, saving time and effort.
For example, a single app could allow drivers to pay for charging, schedule maintenance, and view vehicle diagnostics, all within one platform.
Benefits for EV Charging Infrastructure Providers
Interoperable apps empower charging infrastructure providers by enabling them to offer a wider range of services. Data sharing between apps can create more detailed charging station usage patterns, providing insights into demand and optimizing infrastructure placement. This allows for more efficient resource allocation and improved charging station availability. The ability to directly communicate with drivers’ preferred apps enables charging providers to efficiently manage their network.
Furthermore, the integration of real-time data can ensure that drivers are aware of any potential issues with charging stations, thus enhancing their reliability and customer experience. By offering drivers a comprehensive overview of available stations, interoperability helps in improving utilization rates.
Reduced Complexity and Improved Efficiency in EV Management
Interoperable EV apps significantly reduce the complexity of EV management for all stakeholders. A single point of access for all information simplifies the overall process. Data standardization across various systems enables a more efficient and streamlined approach to vehicle management, maintenance, and charging. For example, real-time data exchange on charging station availability and pricing can enable dynamic pricing strategies, maximizing the efficiency of charging infrastructure.
This interoperability fosters a more efficient and integrated EV ecosystem, leading to substantial cost savings for all involved.
Challenges to Interoperability: Interoperable EV Apps

Achieving seamless interoperability for electric vehicle (EV) applications necessitates overcoming several hurdles. These challenges range from technical limitations in data exchange to security concerns surrounding sensitive vehicle information. Addressing these obstacles is crucial for fostering a robust and user-friendly EV ecosystem.
Technical Hurdles in Data Exchange
The complexities of EV systems and the diversity of data formats employed by various manufacturers pose significant technical hurdles. Different communication protocols, data structures, and message formats can hinder seamless data exchange between different EV applications. Standardization efforts are necessary to ensure interoperability across diverse platforms.
App Platform and Standard Variations
The fragmentation of app platforms (iOS, Android, web-based) and their respective standards significantly impacts interoperability. Different platforms have varying API specifications, security protocols, and performance characteristics, creating compatibility issues. This necessitates the development of platform-agnostic solutions to enable consistent functionality across diverse ecosystems.
Data Format Standardization
Standardization of data formats is essential for interoperability. Different EV manufacturers often employ unique data formats for storing and transmitting information. A lack of common data formats creates difficulties in extracting and utilizing data from various sources. Developing a standardized data exchange format is crucial to enabling seamless integration of data from various EV apps. For instance, inconsistent representations of battery levels or charging statuses can complicate the development of unified charging apps.
The lack of standardized formats can also hinder the ability of third-party developers to create applications that effectively utilize the data from multiple manufacturers.
Security Concerns
Security is paramount when exchanging sensitive vehicle data. Concerns about unauthorized access, data breaches, and malicious use of vehicle information must be addressed. Robust encryption and secure communication channels are crucial to protect sensitive data during transmission and storage. Implementing stringent security protocols and conducting rigorous security assessments are vital for building trust and confidence in interoperable EV applications.
Real-world examples like the growing number of cyberattacks on connected devices underscore the need for comprehensive security measures in EV applications. The potential for unauthorized access to vehicle control systems, potentially leading to safety hazards, highlights the critical importance of robust security measures. This requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing secure communication protocols, authentication mechanisms, and rigorous data validation procedures.
Use Cases for Interoperable EV Apps
Interoperable EV applications promise a more seamless and integrated experience for electric vehicle owners. This is achieved by enabling communication and data exchange between different EV platforms, charging networks, and maintenance providers. This approach unlocks new possibilities for optimizing various aspects of EV ownership.
Examples of Interoperable EV App Use
Interoperable EV applications offer numerous use cases that span the entire EV lifecycle. These range from the initial purchase to the ongoing maintenance and usage of the vehicle. By enabling seamless data exchange, these applications can create a more convenient and efficient experience.
- Seamless Charging Experiences: Interoperable applications can facilitate seamless charging across diverse networks. Drivers can easily locate available chargers, compare pricing, and initiate charging sessions without switching between multiple apps. This streamlined experience eliminates the need for individual accounts and logins for different charging providers.
- Integrated Vehicle Diagnostics and Maintenance: Interoperable applications can integrate vehicle diagnostics with maintenance services. Drivers can access real-time vehicle data, such as battery health and component performance, directly from their maintenance provider’s app. This facilitates proactive maintenance scheduling and informed decisions about necessary repairs. The application can provide detailed diagnostic information, enabling efficient and accurate maintenance procedures, avoiding costly and unnecessary repairs.
- Real-Time Vehicle Information Sharing: Interoperable applications can enable the sharing of real-time vehicle information with other users. This could include features like sharing charging station availability or route recommendations based on vehicle range and charging infrastructure. This can be particularly useful for fleet management or for sharing charging station information with friends or family, improving community engagement within the EV ecosystem.
This functionality is also helpful in emergency situations, enabling immediate and effective communication regarding vehicle status.
Seamless Charging Experience Across Networks
A key benefit of interoperability is the ability to access charging stations across different networks using a single application. Imagine a driver with an EV needing to charge while traveling. With an interoperable app, they can locate all available charging stations along their route, regardless of the charging network provider. The app will display real-time pricing, estimated wait times, and charger availability.
The driver can select the most suitable charger, initiate the charging session directly through the app, and manage payment effortlessly, all within the same interface.
Integrating Vehicle Diagnostics with Maintenance Services
Imagine an EV owner experiencing a performance issue. Using an interoperable app, they can access real-time vehicle diagnostics, providing detailed information about the vehicle’s health. This data can be shared seamlessly with their chosen maintenance provider, enabling them to diagnose the problem remotely. The maintenance provider can use this data to recommend necessary repairs, schedule an appointment, and ensure accurate parts ordering.
This proactive approach minimizes downtime and reduces the likelihood of unnecessary repairs.
Sharing Real-Time Vehicle Information with Other Users
Interoperable applications can facilitate the sharing of real-time vehicle information. For example, a driver could share information about charging station availability with friends or family members, or a fleet manager could track the location and status of their vehicles. This capability is beneficial for shared vehicles or for coordinating multiple drivers. Furthermore, this can be beneficial in emergency situations, allowing for quick and effective communication about the vehicle’s status.
Sharing real-time data enhances the efficiency of vehicle usage and promotes community support within the EV community.
Standards and Protocols
Establishing common standards and protocols is crucial for seamless data exchange between different EV charging and management systems. These standards enable interoperability, allowing various EV apps to access and utilize information from different sources, ultimately improving the user experience. This section explores existing standards, protocols, and the role of industry bodies in promoting interoperability, along with potential future directions.
Existing Standards for EV Data Communication
A variety of standards are already in use for EV data communication. These standards facilitate information sharing between different components of the EV ecosystem, like charging stations, vehicles, and management systems. This allows for the exchange of critical data such as charging status, location information, and pricing details.
- Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP): This widely adopted protocol facilitates communication between charging stations and the central management system. It allows for the exchange of real-time information regarding charging sessions, such as session start, status updates, and completion. OCPP versions 1.6 and 2.0 are commonly implemented, with each version offering increasing sophistication in data exchange capabilities.
- ISO 15118: This international standard defines communication protocols for the vehicle-to-grid (V2G) and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication, including data formats and procedures for exchanging data between the EV and the charging infrastructure. It covers a broader range of communication aspects compared to OCPP, enabling more complex interactions.
- SAE J1939: This standard focuses on communication between different components within a vehicle, including engine controls, transmission systems, and other subsystems. While not directly related to EV apps, it’s crucial for the broader ecosystem, providing communication channels for essential vehicle data.
Comparison of Communication Protocols
Different protocols cater to specific aspects of EV data communication. A direct comparison of protocols like OCPP, ISO 15118, and SAE J1939 highlights their distinct roles and functionalities. Understanding these differences is crucial for designing interoperable EV apps that effectively leverage the available resources.
| Protocol | Focus | Scope | Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| OCPP | Charging station communication | Charging session management | Medium |
| ISO 15118 | Vehicle-to-grid and vehicle-to-everything communication | Broader vehicle-infrastructure interaction | High |
| SAE J1939 | Vehicle component communication | Vehicle internal systems | Medium |
Role of Industry Bodies in Promoting Interoperability
Industry bodies play a critical role in standardizing communication protocols and fostering collaboration between stakeholders. Their efforts are instrumental in ensuring compatibility between different EV systems.
- SAE International: This organization plays a significant role in defining standards for the automotive industry, including vehicle communication protocols. Their standards are crucial for promoting compatibility between different components.
- ISO (International Organization for Standardization): ISO sets international standards for various industries, including automotive. ISO 15118, for instance, demonstrates their contribution to EV interoperability.
Potential Future Standards for EV App Interoperability
The future of EV app interoperability will likely involve further standardization efforts. Emerging technologies and evolving user needs will shape the requirements for future standards.
- Centralized data platforms: A single platform that aggregates data from various sources could facilitate streamlined access for EV apps. This would enhance user experience by providing a consolidated view of charging options and vehicle status.
- Blockchain-based solutions: Blockchain technology could enhance transparency and security in EV data exchange, enabling secure transactions and verified information.
- API-based communication: Defining comprehensive Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) would enable different apps to easily interact with various charging infrastructure providers.
Implementation Strategies
Implementing interoperable EV apps requires a strategic approach encompassing various facets of development, security, and collaboration. A well-defined implementation plan is crucial for ensuring seamless integration and user experience across different charging networks and vehicle models. Successful implementation hinges on clear communication channels, robust security protocols, and a commitment to ongoing maintenance and improvement.The key to a successful interoperable EV app lies in a structured methodology that prioritizes compatibility, security, and user experience.
This involves careful consideration of various factors from initial design to long-term maintenance. This detailed approach guides developers through the process, ensuring a final product that effectively serves the needs of both drivers and charging infrastructure providers.
Interoperable EV apps are crucial for a seamless user experience. Think about how a great ceramic coating ceramic coating protects your vehicle; similarly, these apps need to work well together to provide a consistent and integrated platform for EV owners. Ultimately, these apps are key to the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
Methods for Implementing Interoperable EV Apps
Implementing interoperable EV apps requires a multi-faceted approach that combines technical expertise with a clear understanding of industry standards and user expectations. The most effective strategies involve adhering to established standards, utilizing secure data exchange protocols, and fostering collaboration among stakeholders. Crucially, rigorous testing is essential to ensure compatibility across different platforms and devices.
- Adherence to Open Standards: A crucial component of interoperability is strict adherence to open standards for communication protocols and data formats. This ensures that various charging networks and vehicle manufacturers can seamlessly exchange information. Examples of relevant standards include OCPP (Open Charge Point Protocol) and other industry-recognized protocols.
- Secure Data Exchange Protocols: Data security is paramount in any interoperable system. Implementing secure protocols like TLS (Transport Layer Security) for data transmission is critical to protect sensitive information, such as payment details and vehicle diagnostics. Robust encryption methods should be employed to safeguard against unauthorized access and manipulation of data.
- Modular Design: Designing the application with modular components promotes flexibility and maintainability. This modular approach allows for easier updates and integration of new features or charging networks without disrupting the entire system.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Developing an Interoperable EV App
A structured development process is essential for building a successful interoperable EV app. This detailed procedure ensures that the app meets the needs of diverse stakeholders and adheres to established standards.
- Requirements Gathering: Define the specific functionalities and features required by users and charging network operators. This crucial initial step involves thorough market research and user interviews to identify key requirements and address potential pain points.
- API Design: Design APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that allow for seamless communication between the app and various charging networks. Thorough API design is crucial for future scalability and integration with new networks.
- Component Development: Develop individual components of the app, ensuring they adhere to established standards and security protocols. This includes integrating with payment gateways, location services, and vehicle communication interfaces.
- Testing and Validation: Rigorous testing is crucial to validate compatibility across different charging networks and vehicle models. This includes testing for performance, security, and user experience on various platforms.
- Deployment and Maintenance: Deploy the app and establish a maintenance plan to ensure continuous updates, bug fixes, and support for new features. A continuous improvement process is essential to adapt to evolving needs and maintain user satisfaction.
Potential Partnerships Between App Developers and Charging Networks
Strategic partnerships between app developers and charging networks are crucial for fostering interoperability. These collaborations provide mutual benefits, leading to improved user experience and wider adoption of EV charging infrastructure.
- Shared Resources: Sharing data, resources, and expertise fosters a collaborative environment. This exchange of information can be invaluable for optimizing the app’s functionality and addressing potential issues.
- Joint Marketing and Promotion: Joint marketing efforts can expand the reach of both the app and the charging network, resulting in a broader user base and increased adoption.
- Data Exchange Agreements: Establish clear data exchange agreements to define how data is shared, stored, and secured. These agreements are critical to maintain trust and ensure compliance with privacy regulations.
Different Approaches for Data Exchange Security
Data security is paramount in interoperable EV apps. Implementing robust security measures protects sensitive information and maintains user trust.
- Encryption: Employing encryption protocols, such as TLS, ensures that data exchanged between the app and charging networks is protected from unauthorized access. This safeguards payment information and vehicle diagnostics.
- Authentication and Authorization: Implement robust authentication and authorization mechanisms to verify user identities and grant access to specific functionalities. This ensures that only authorized users can access sensitive data.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address potential vulnerabilities. This proactive approach helps to prevent security breaches and maintain the integrity of the system.
Security Considerations
Ensuring the security of data exchanged between various EV applications is paramount. Robust security measures are critical to protecting sensitive user information and maintaining the integrity of the system. This includes safeguarding vehicle data, charging session details, and user credentials. The integrity and confidentiality of this data are essential for building trust and fostering a secure environment for all users.Implementing robust security protocols is crucial for maintaining user trust and preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Comprehensive encryption, secure authentication mechanisms, and access control measures are essential elements of a secure interoperable EV app ecosystem. This ensures the protection of user information and prevents malicious activities.
Data Protection Measures, Interoperable EV apps
Protecting user data requires a multi-layered approach. This includes implementing strong encryption, robust access control mechanisms, and secure authentication protocols. These measures work together to create a secure environment for sensitive data transmission and storage.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting data at rest and in transit is vital. This prevents unauthorized access even if data is intercepted. Advanced encryption standards (AES) and TLS/SSL protocols are common choices for data encryption. These protocols protect the confidentiality of user information during transmission.
- Secure Storage: Securely storing sensitive data is equally important. Data should be encrypted at rest using strong encryption algorithms. Data access should be restricted to authorized personnel with the appropriate security clearance.
- Regular Security Audits: Regular security audits are necessary to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities. These audits should be performed periodically to ensure the security measures remain effective and up-to-date. Regular security testing and vulnerability assessments should be part of a continuous improvement strategy.
Encryption Methods for Secure Data Transmission
Several encryption methods can be used to secure data transmission between EV applications. The choice depends on the sensitivity of the data and the specific requirements of the application.
- Advanced Encryption Standard (AES): A widely adopted symmetric encryption algorithm. It offers strong encryption and is suitable for various data types, including user credentials and vehicle telemetry data.
- Transport Layer Security (TLS): A protocol for securing communication channels over the internet. TLS is often used to encrypt data transmitted between EV applications and servers. It ensures secure communication and protects data from eavesdropping.
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKI): A system for managing digital certificates and public/private key pairs. PKI provides a secure way to authenticate users and devices and ensures the integrity of data exchanged between applications.
Access Control Mechanisms
Access control mechanisms are essential for restricting access to sensitive data and resources. These mechanisms ensure only authorized users can access specific information.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): A method for granting access based on user roles and responsibilities. This ensures only authorized users with specific roles can access particular data or perform certain actions. For instance, a customer service representative might have access to user account information but not vehicle diagnostics.
- Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC): A method for granting access based on attributes of users, resources, and environments. ABAC provides a more granular and flexible approach to access control. It considers factors like user location, time of day, and device type to determine access permissions.
Authentication Protocols
Authentication protocols verify the identity of users and devices to ensure secure data exchange. They prevent unauthorized access and maintain the integrity of the system.
- OAuth 2.0: A widely used authorization framework that allows applications to access user data from other services without requiring users to share their credentials directly. This approach enhances security and user privacy.
- OpenID Connect (OIDC): An identity layer built on top of OAuth 2.0. It allows applications to verify user identities and obtain information about users from an identity provider. This simplifies user authentication and access control.
Future Trends
The development of interoperable EV apps is poised for significant advancements, driven by emerging technologies and a growing demand for seamless user experiences. These advancements will not only enhance the functionality of individual apps but also create a more interconnected and efficient ecosystem for electric vehicle users. The future will see a convergence of technologies, fostering innovation and potentially revolutionizing how EV owners interact with their vehicles and the broader charging infrastructure.
Emerging Trends in EV App Development
Several trends are shaping the future of interoperable EV apps. The demand for greater functionality, combined with the increasing sophistication of mobile devices, is driving the development of more complex and integrated applications. This includes features such as real-time location tracking, dynamic pricing, and advanced route planning, all facilitated by seamless communication between different platforms. Furthermore, the growing need for personalized user experiences will likely lead to more sophisticated algorithms and data analysis, enabling apps to better anticipate user needs and provide tailored recommendations.
Impact of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology presents a compelling opportunity to enhance the security and transparency of interoperable EV apps. Its decentralized nature can facilitate secure transactions and data sharing, potentially eliminating single points of failure and fostering greater trust among users. For instance, blockchain can create a transparent record of charging transactions, allowing users to easily verify pricing and identify potential fraudulent activities.
Moreover, blockchain can support the creation of decentralized charging networks, giving users more control over their charging experiences and potentially lowering costs.
Emerging Technologies
Several emerging technologies are poised to play a crucial role in the development of interoperable EV apps. These include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered algorithms can enhance features like dynamic route planning, personalized recommendations, and predictive maintenance, improving the overall user experience and optimizing resource allocation.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT integration will facilitate seamless communication between various devices, including EV charging stations, vehicle sensors, and user apps. This will lead to more efficient and intelligent charging networks.
- 5G and Beyond: Faster and more reliable wireless communication technologies, like 5G and future iterations, will enable real-time data exchange, supporting complex features like real-time vehicle diagnostics and advanced remote control.
Predictions for the Future of EV App Interoperability
The future of EV app interoperability is expected to be characterized by increased integration and user-centric design. We predict that:
- Seamless integration of diverse platforms: Interoperable apps will seamlessly integrate data from various sources, offering a holistic view of charging options, vehicle maintenance, and other related services.
- Increased user personalization: Apps will leverage AI to provide personalized recommendations and insights, tailored to individual user preferences and driving habits.
- Enhanced security and trust: Blockchain technology and advanced security protocols will contribute to a more secure and transparent environment for EV users, fostering greater trust in the system.
Illustrative Examples
Interoperable EV apps promise seamless integration across various functionalities, from charging to navigation. These examples highlight the potential benefits of standardized communication protocols and data formats. Illustrative cases show how interoperability can streamline user experiences and foster innovation within the EV ecosystem.
EV App Functionality Examples
This table presents examples of different EV app functionalities and their potential integration with interoperable standards. It demonstrates how diverse functionalities can be connected and managed through a shared platform.
| Functionality | Description | Integration Aspects | Communication Protocols |
|---|---|---|---|
| Charging | Finding and booking charging sessions, managing charging profiles, and monitoring charging status. | Integrating with various charging station providers, allowing users to seamlessly select charging stations from different networks. | Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP), ISO 15118, or similar standards. |
| Navigation | Providing real-time route planning, considering charging station locations, and optimizing charging stops. | Integrating with mapping services and real-time traffic data to account for charging availability and estimated time of arrival (ETA). | GPS, map data formats, and communication with charging station networks. |
| Vehicle Diagnostics | Monitoring vehicle health, diagnosing potential issues, and providing maintenance recommendations. | Accessing vehicle data through standardized APIs, enabling seamless integration with diagnostic tools. | Vehicle-specific protocols (e.g., OBD-II) and standardized data formats. |
| Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) | Managing energy flow between the vehicle and the grid, enabling vehicle-to-grid services. | Enabling the vehicle to act as a power source, offering benefits for grid stability and energy management. | V2G communication protocols, possibly involving smart grids. |
Interoperability Standards Advantages and Disadvantages
This table summarizes the advantages and disadvantages of various interoperability standards, providing a comparative overview for potential implementations.
| Standard | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP) | Widely adopted, mature, and well-documented standard for charging station communication. | Can be complex to implement for certain functionalities, might not cover all aspects of V2G. |
| ISO 15118 | Comprehensive standard for communication between vehicles and charging stations, covering a broad range of functionalities. | Relatively newer, implementation may require more resources. |
| OBD-II | Common standard for vehicle diagnostics, widely supported by vehicles. | May not be sufficient for complex diagnostic needs, not specifically designed for EV-specific functionalities. |
Interoperable Charging Network Use Case
A specific use case of an interoperable charging network demonstrates the benefits for drivers. Consider a scenario where a driver, using a dedicated app, can plan a cross-country trip, accounting for charging availability along the route.
- Optimized Route Planning: The app considers charging station locations, availability, and charging times, generating a route that minimizes charging downtime.
- Seamless Charging Experience: The app automatically connects with charging stations from different networks, allowing the driver to select the most suitable station based on factors like price and speed.
- Real-time Charging Information: The app provides real-time updates on charging station availability and estimated charging time, enhancing user experience.
- Enhanced Driver Confidence: Drivers know their charging needs are addressed during their trip, reducing anxiety about running out of charge.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Optimized routes and efficient charging minimize range anxiety and fuel consumption, improving overall sustainability.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, interoperable EV apps represent a significant leap forward in electric vehicle technology. By overcoming challenges and fostering collaboration, the industry can unlock a more convenient, efficient, and secure experience for EV owners. The future of EV mobility depends on our collective ability to create a truly interconnected ecosystem.
General Inquiries
What are the key benefits of interoperable EV apps for drivers?
Drivers benefit from a wider range of charging options, seamless data access (like vehicle diagnostics), and potentially lower costs due to reduced complexity in managing their vehicles.
What are some common technical hurdles to interoperability?
Different app platforms, lack of standardized data formats, and security concerns regarding sensitive vehicle data are significant technical hurdles. Ensuring compatibility across various devices and software versions also poses a challenge.
How does blockchain technology potentially impact interoperability?
Blockchain could enhance security and transparency by providing a secure and immutable record of data transactions, potentially fostering trust among users and providers.
What role do industry bodies play in promoting interoperability?
Industry bodies can establish and enforce standards, fostering communication and collaboration between app developers and charging networks, ensuring a common platform.





